Getting Started
Implementing a framework with a template
Starting with a template
This article describes the implementation of a compliance framework when you start with a prepared template. Your Tidal Control environment has already been set up with all required elements for the chosen framework.
Did you start without a template or want to add a new framework? See the article Initialising framework without template.
Framework ready for use
Prepared framework template
Your Tidal Control environment is set up with a complete framework template:
- Controls are prepared and linked to the chosen framework
- Risks are identified and already linked to relevant controls
- Implementation tasks are automatically generated per control
- Policy templates are available and linked to controls via tests
- Framework connections between all elements are already established
All building blocks are present and connected - you can start implementation immediately.
Getting started
- Go to Frameworks section
- Select desired framework (e.g. ISO 27001)
- Framework shows implementation status and controls to implement
- Begin with first implementation steps:
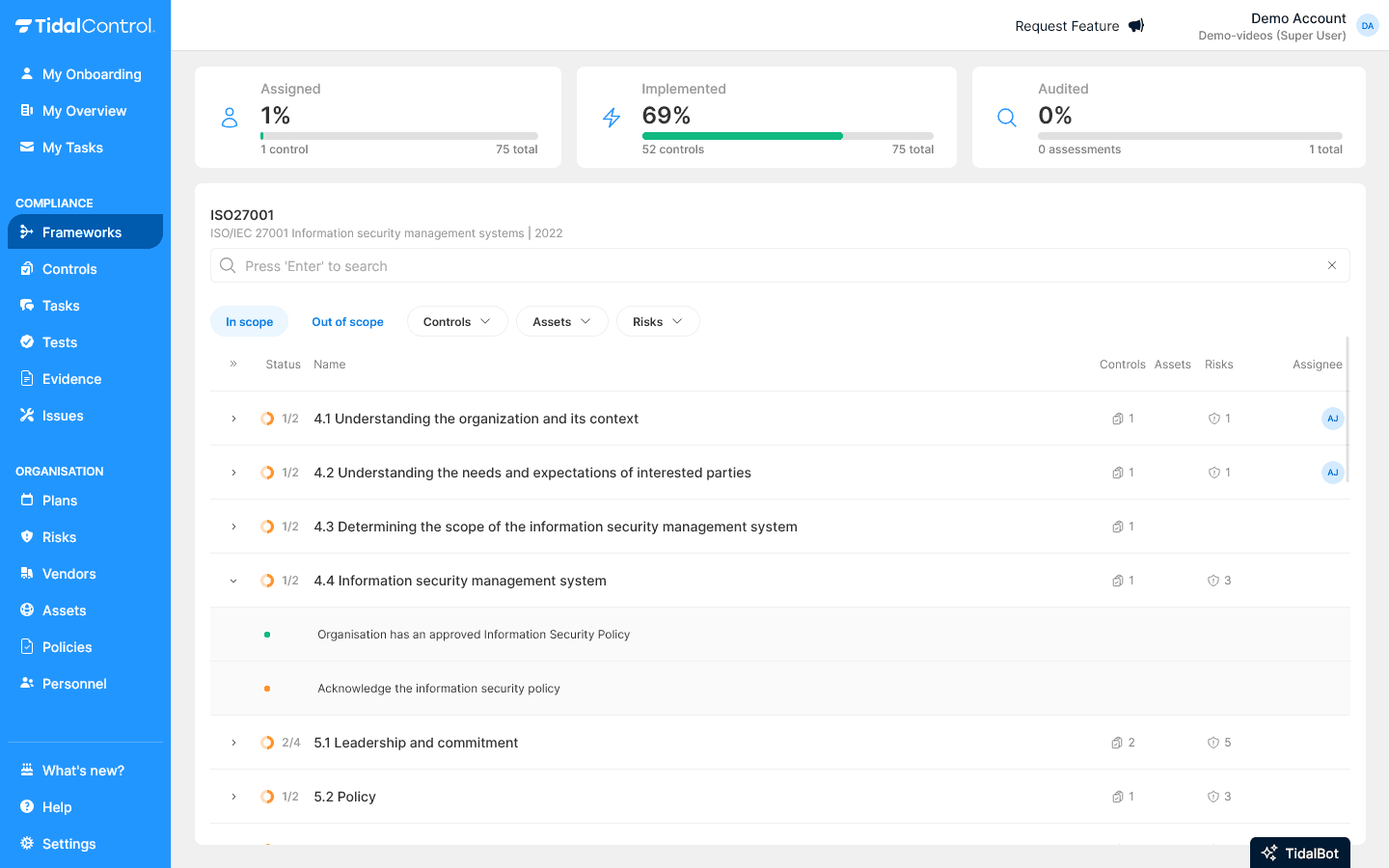
For more information about frameworks, see Frameworks getting started.
PDCA implementation cycle
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) is a proven methodology for systematic compliance implementation. This cyclical approach ensures structural improvement and sustainable compliance:
- Plan - Strategic planning, risk analysis and scope determination
- Do - Execution of controls and policy implementation
- Check - Monitoring, testing and validation of effectiveness
- Act - Improvement actions and optimisation for next cycle
By executing this cycle you create a working information security management system (ISMS). The cycle then repeats annually for continuous improvement of your compliance posture.
The Controls overview page contains a 'Phase' filter where you can filter on the Plan-Do-Check-Act phase.
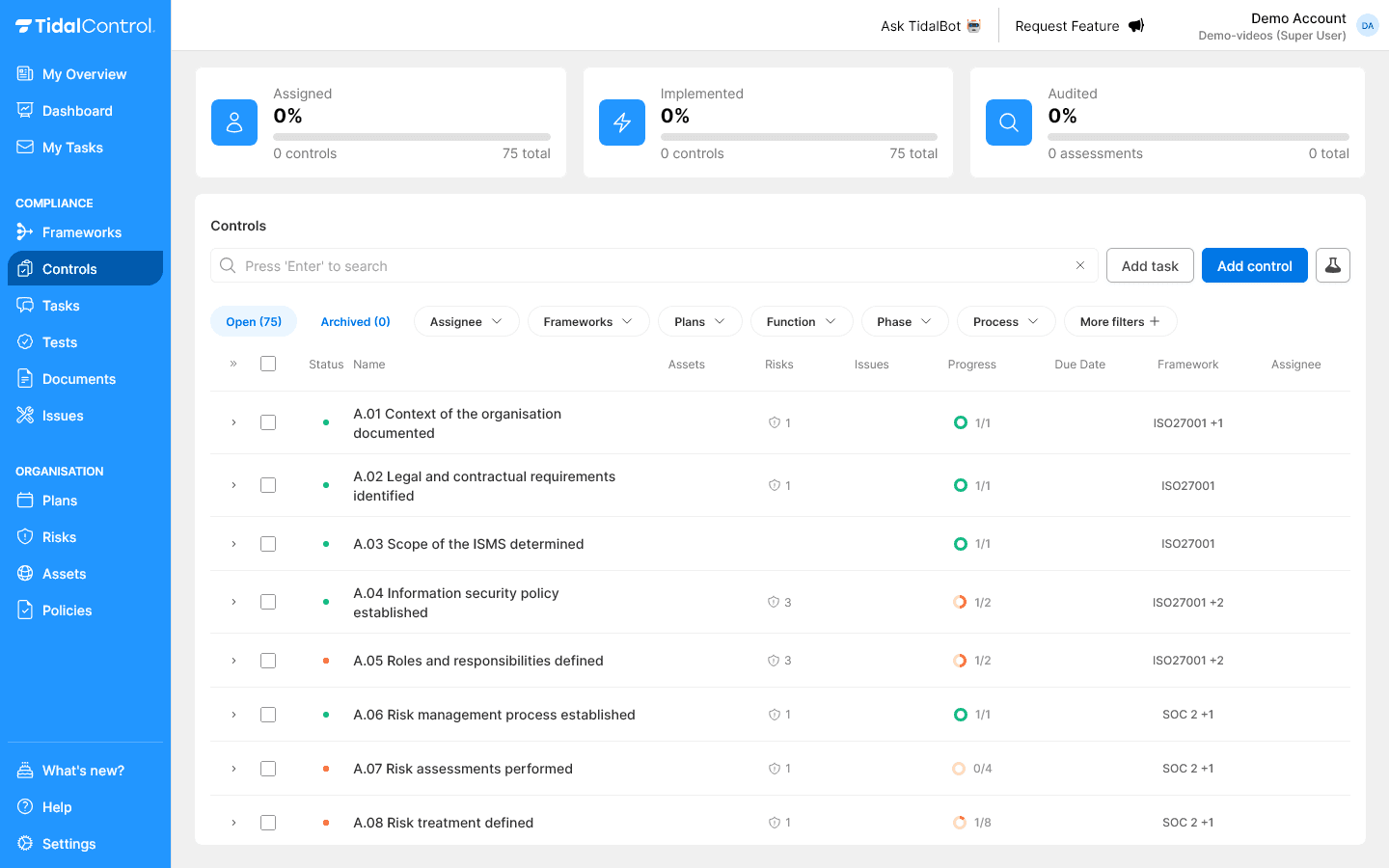
Begin your implementation with the Controls in the Plan phase.
For more information about controls, see Controls getting started.
Plan phase
In the Plan phase you lay the foundations for your Information Security Management System (ISMS). Because you're starting with a prepared template, most risks and controls are already identified and linked. In this phase you'll personalise this setup to your own organisation.
Your focus is on:
- Contextualising predefined elements to your organisation
- Validating whether template risks and controls are relevant for your situation
- Adjusting scope and priorities where needed
- Preparing the implementation team and resources
The following steps help you move from a generic template to an organisation-specific implementation plan.
Step 1: Fill in business profile and conduct context analysis
This step answers the following questions:
- Organisation description - What does your business do, which products and services?
- Business environment - Which people, technologies, locations and processes are needed for this?
- Stakeholder mapping - Who are important parties (customers, suppliers, regulators) and what do they expect from you regarding information security?
- Threat identification - Which information security risks threaten these interests?
How to execute:
-
Go to Policies section
-
Find and select 'Context of the Organisation' from the policies list.
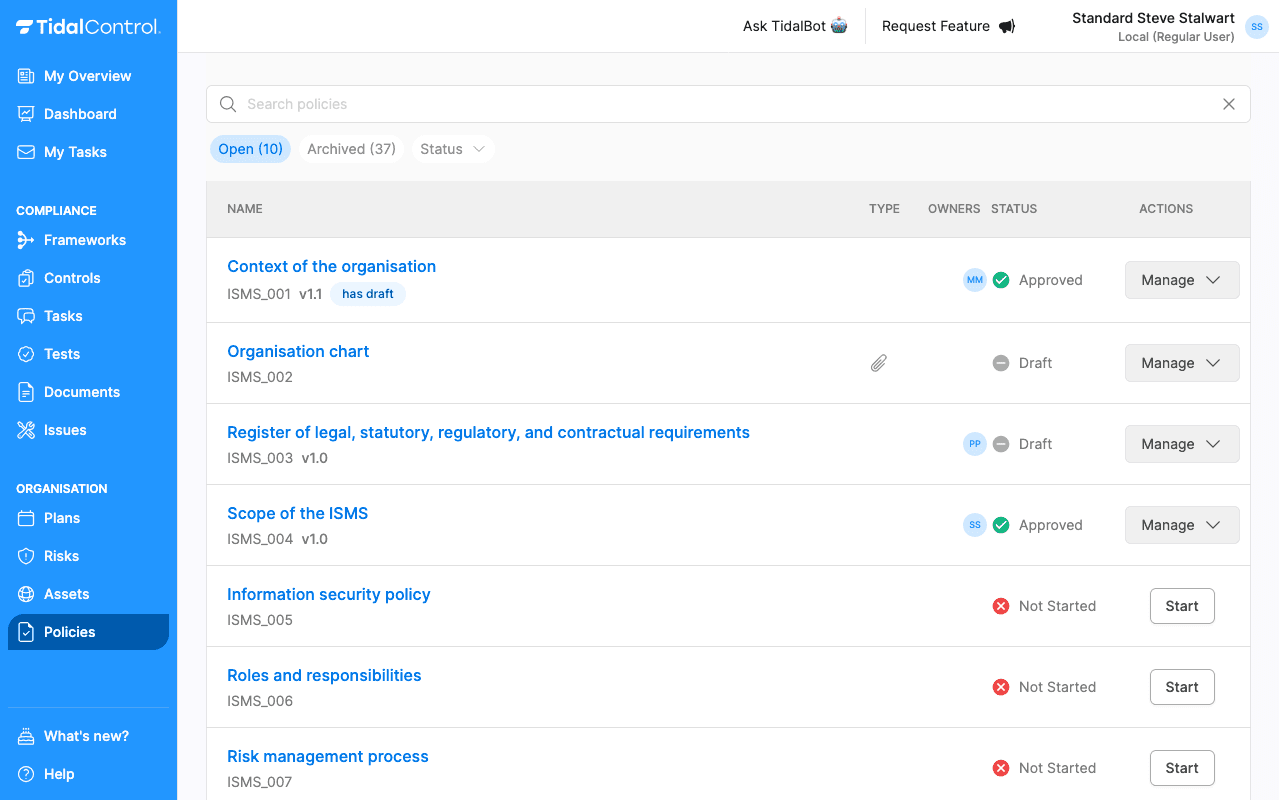
-
Select 'Edit' top right of the screen to fill in the form
-
Complete the document according to instructions in the yellow box
-
Select 'Update' to save the form (interim)
-
Select 'Approve' to approve the form and complete this task.
Step 2: Inventory external requirements
This step answers the following questions:
- Laws and regulations - Which legal obligations apply to your organisation?
- Standards - Which industry-specific standards are applicable?
- Contractual obligations - Which information security requirements do customers place on your organisation?
How to execute:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Register of legal, statutory, regulatory, and contractual agreements' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of the screen to fill in the form
- Review the first block - Review the predefined list of laws and regulations and mark what applies to your organisation
- Complete the second block - Add industry-specific standards relevant to your sector
- Document the third block - Inventory information security requirements from customer contracts and agreements
- Select 'Update' to save the form (interim)
- Select 'Approve' to approve the document and complete this task
Step 3: Create asset inventory and classify assets
This step answers the following questions:
- Asset identification - Which systems, data and processes are critical for your organisation?
- Asset ownership - Who is responsible for each asset?
- Classification levels - What is the security value per asset?
- Business impact - What happens with loss of availability, integrity or confidentiality?
How to execute:
-
Go to Assets section
-
Click "Add Asset" to add new assets
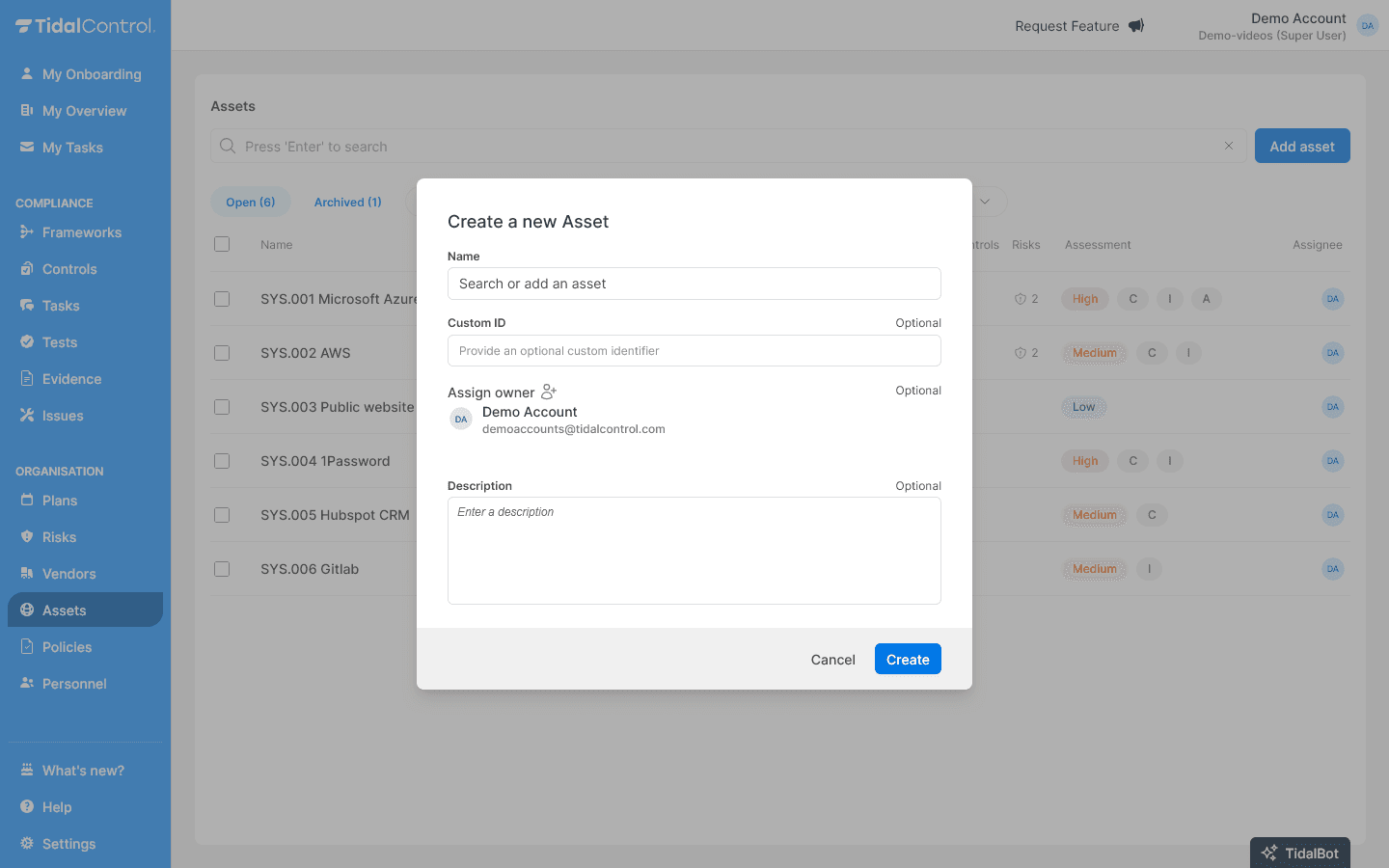
-
For each asset you fill in:
- Asset name and description
- Asset type (e.g. System, Data, Process)
- Owner - Assign a responsible person
- Classification - Determine security level (Low, Medium, High)
-
Repeat this process for all critical assets
-
Review the complete list - Are all essential assets included?
For more information about asset management, see Assets getting started.
Step 4: Conduct risk analysis
This step answers the following questions:
- Relevant risks - What are the risks to information security?
- Risk levels - What is the likelihood that risks materialise, and how high is the impact for the organisation if they lead to damage?
- Risk treatment strategy - Do we accept these risks, or will we do something about them (reduce, transfer, or avoid)?
How to execute:
- Go to Risks section
- Open predefined risks from framework
- Assess each risk against your business context:
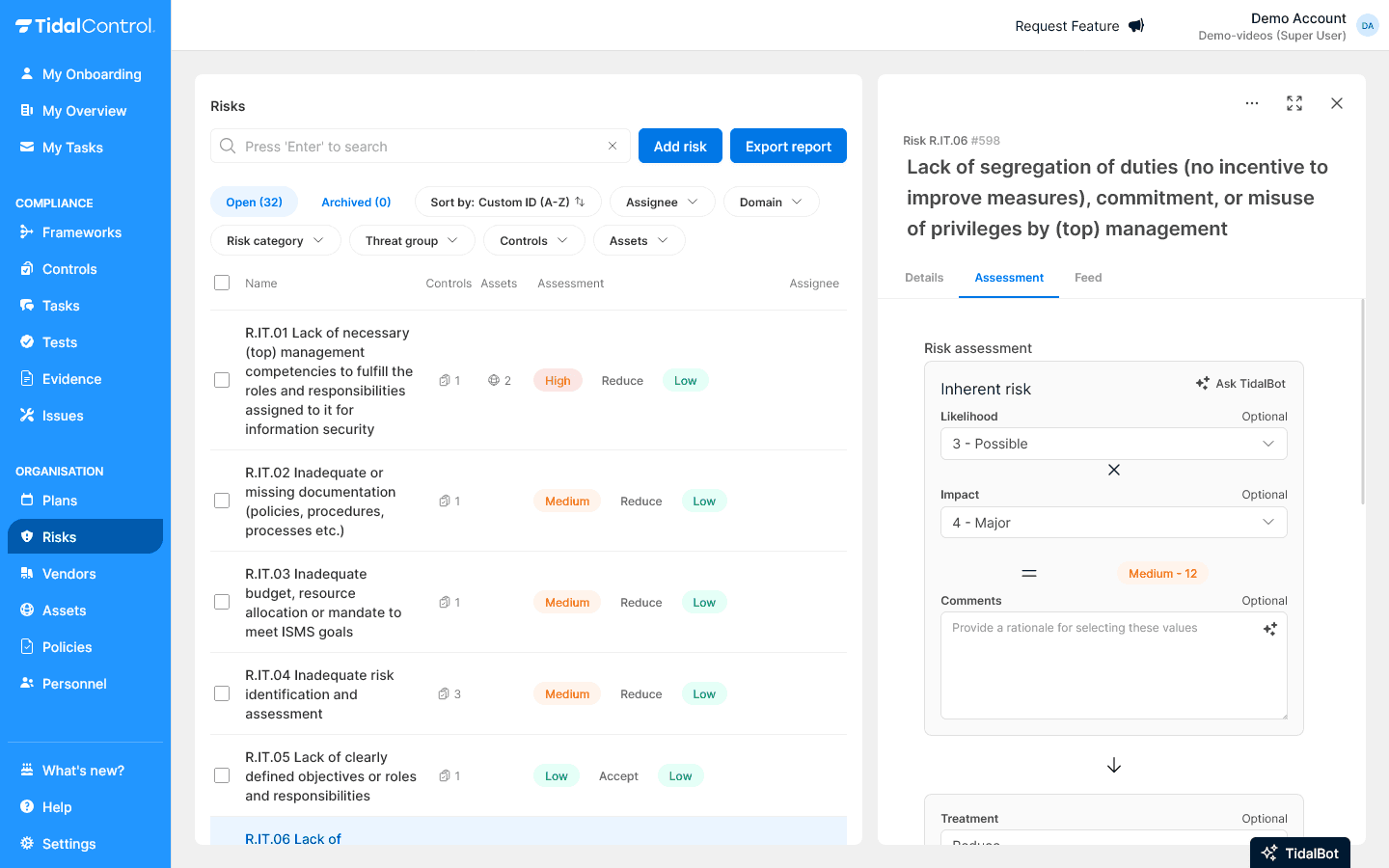
For more information about risk management, see Risks.
- Likelihood - How likely is the risk to occur?
- Impact - What is business impact when occurring?
- Risk level is automatically calculated
- Risk treatment Select a treatment option - If 'reduce': Review relevant controls to reduce this risk
- Residual risk level determine residual risk after implementing treatment option
- Add organisation-specific risks if needed
- (optional) Link risks to specific Assets if desired
Step 5: Finalise and document scope
This step answers the following questions:
- Scope of assets: processes, locations, and business units
- Scope of controls - Which controls are or aren't relevant for identified risks?
- Justification document this for audit purposes
How to execute:
First we'll finalise the Controls scope:
- Go to Controls section
- Click 'More filters' at top of screen
- Click 'Risks' filter
- Select 'No risk assigned' in dropdown
 5. Review the Controls in this list:
5. Review the Controls in this list:
- Link risks to Controls you deem necessary for information security
- Consider archiving all controls where after evaluation still no risk is linked
ISO 27001 requires that all controls (in scope and out of scope) contain justification.
Tidal uses the following strategy:
- In Scope: Justification follows from linking with one or more risks.
- Out of Scope: Justification follows from absence of risk linking, but must also be specifically documented in 'Statement of Applicability', found in the Policies section.
Now we'll finalise the Statement of Applicability:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Statement of Applicability' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of screen
- Review the document - It's already largely completed based on your template
- Mark out-of-scope controls:
- Identify controls not applicable to your organisation
- Add justification - Document why each control isn't relevant
- Mark as 'Not Applicable' in document
- Verification step - Check if out-of-scope list matches archived controls in Tidal:
- Open second tab with Controls section
- Filter on Archived controls
- Compare both lists for consistency
- Select 'Update' to save changes
- Select 'Approve' to approve document
Finally we'll finalise formal scope documentation:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Scope of the ISMS' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of screen to fill in the form
- Document the following elements:
- Processes - Which business processes fall within scope?
- Locations - Which sites and offices are included?
- Assets - Which systems and assets are part of the ISMS?
- Organisation units - Which departments and business units fall within scope?
- Select 'Update' to save form
- Select 'Approve' to approve document
Step 6: Approve Information Security Policy
This step answers the following question:
- Organisation commitment - How does the organisation show its commitment to information security and the ISMS?
The Information Security Policy forms the basis of your ISMS and shows management commitment to information security. This policy must be approved by senior management.
How to execute:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Information Security Policy' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of screen to fill in the form
- Review and adapt policy template:
- Check organisation details - Name, sector, and business activities
- Validate scope reference - Does reference to your ISMS scope match?
- Review commitment statements - Do these fit your organisation culture?
- Adapt where needed - Make policy organisation-specific
- Select 'Update' to save form
- Select 'Approve' to approve policy and complete this step
The Information Security Policy must be formally approved by senior management (CEO, directors). Ensure the right person approves the document in Tidal.
Step 7: Assign roles and finalise objectives
This step answers the following questions:
- Who is responsible for what - Which people fulfil key ISMS roles?
- What do we want to achieve - Which concrete objectives does the organisation have for this PDCA cycle?
- How do we measure success - By which criteria can we measure progress?
Fill in Roles & Responsibilities:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Roles & Responsibilities' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of screen
- Fill in ISMS roles table:
- CISO/ISO - Assign Information Security Officer
- DPO - Appoint Data Protection Officer (if applicable)
- Other roles - Fill in additional functions according to your organisation
- Select 'Update' to save form
- Select 'Approve' to approve document
Review Information Security Objectives:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and select 'Information Security Objectives' from the policies list
- Select 'Edit' top right of screen
- For first PDCA cycle:
- Review predefined objectives - These are already filled in for the first cycle
- Adapt where needed - Make goals specific for your organisation context
- Expertise gaps - If additional training is needed for team members, add those as objectives here too
- Validate objectives are SMART - Check success criteria, responsible persons, and timelines are concrete and realistic
- Select 'Update' to save form
- Select 'Approve' to approve document
For second and subsequent PDCA cycles you start with an empty template. Objectives are then determined based on:
- Action points from previous cycle
- Findings from management reviews
- Lessons learned from Check and Act phases
Assign tasks to team:
- Go to Tasks section
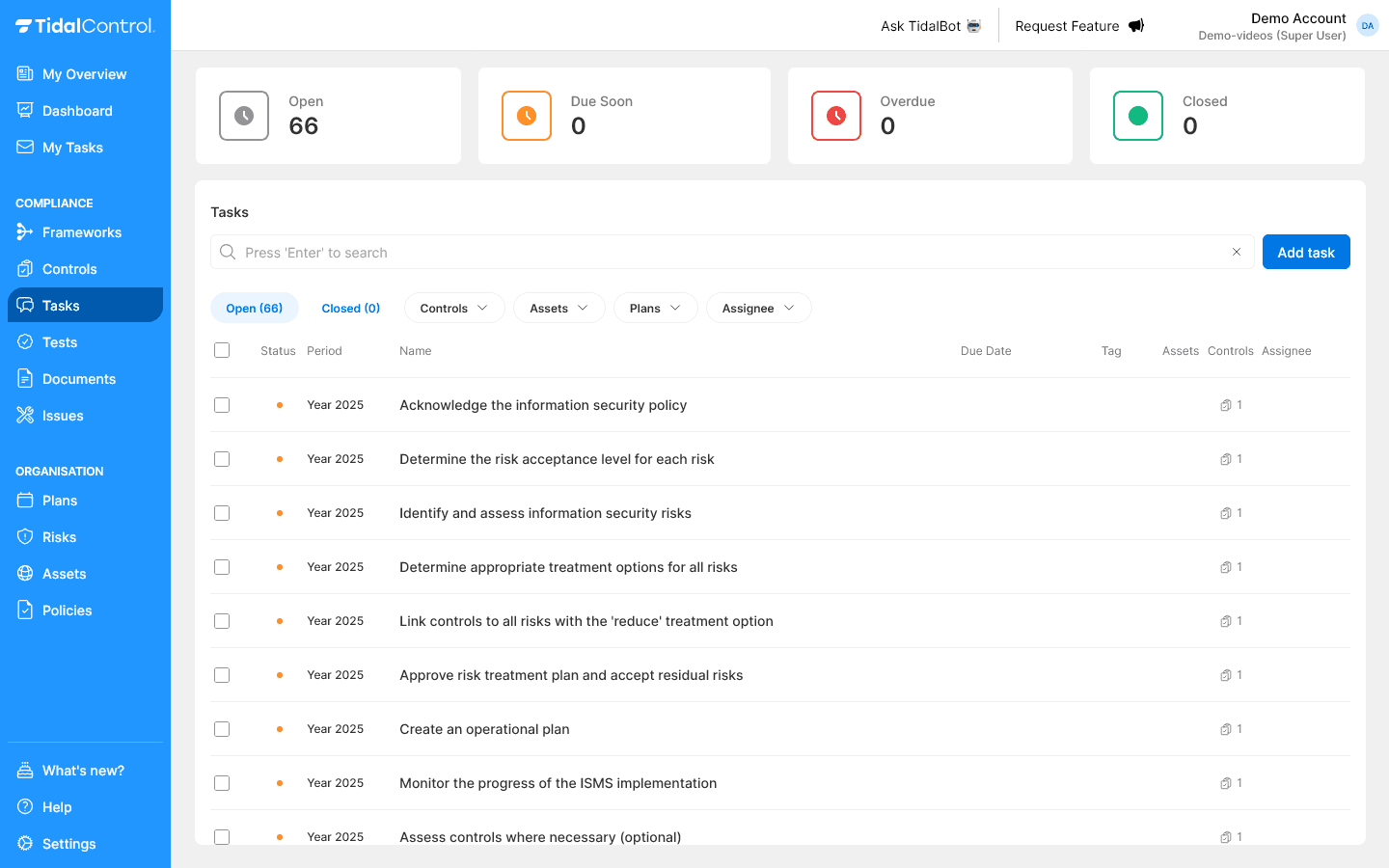
- Filter on framework tasks to show only relevant tasks
- Select tasks requiring manual execution
- Assign owners via "Assign" dropdown per task
- Team receives notifications and can start execution
- Monitor progress via task status updates
For more information about task management, see Tasks
Do phase
In the Do phase you actually execute the planned controls. Because you start with a template, implementation tasks are already prepared and linked to controls. Your focus is on execution and documentation.
Configure and monitor automatic testing
Automate technical controls:
-
Identify relevant systems - AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, GitHub, etc.
-
Go to Integrations section
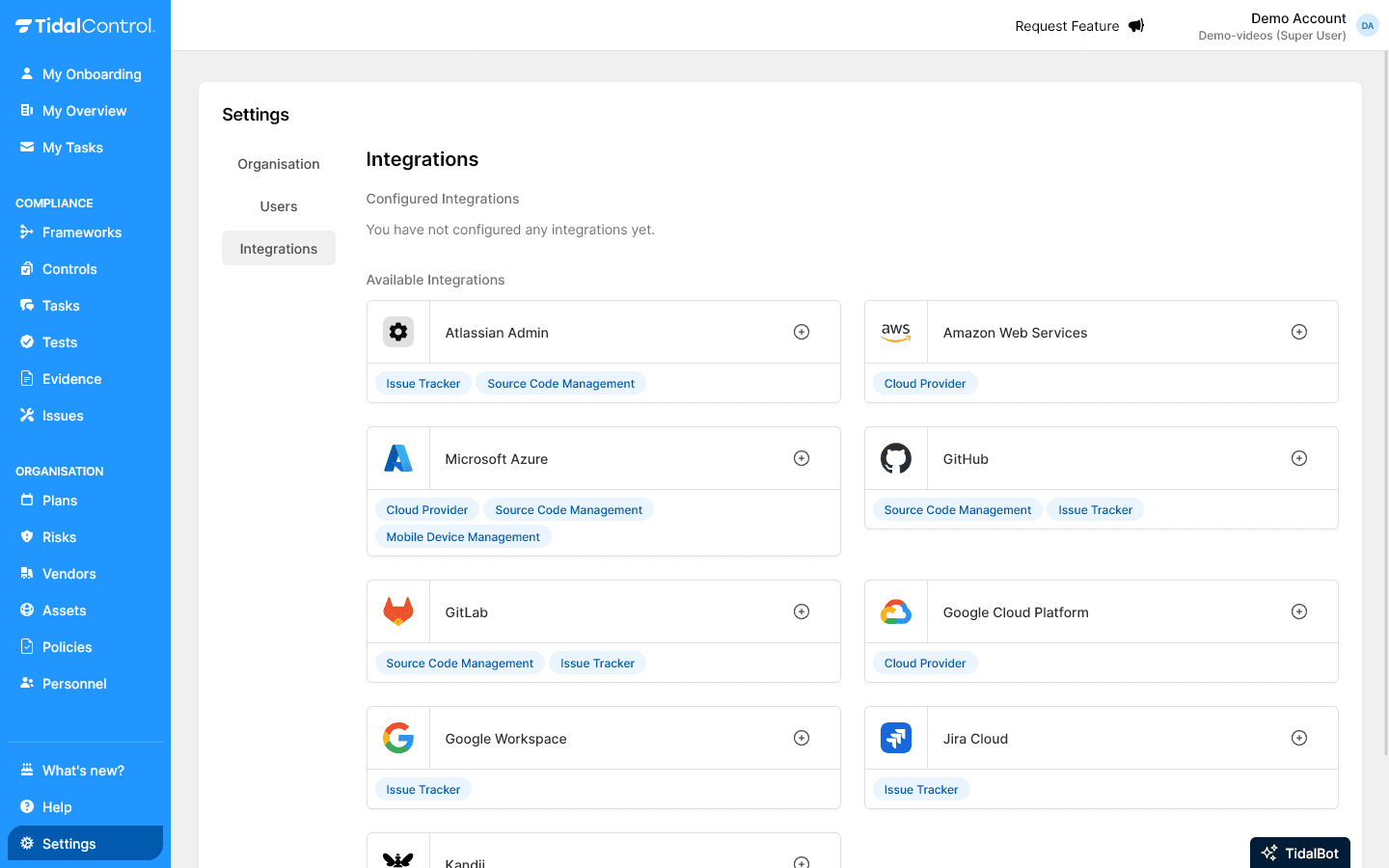
-
Configure integrations for automated compliance tests
-
Test connections - Check data is retrieved correctly
-
Monitor test results - Review pass/fail status for technical controls
-
Address failures - Resolve technical issues where tests fail
For detailed integration setup, see Integrations getting started.
Interpret test results:
-
Go to Tests section
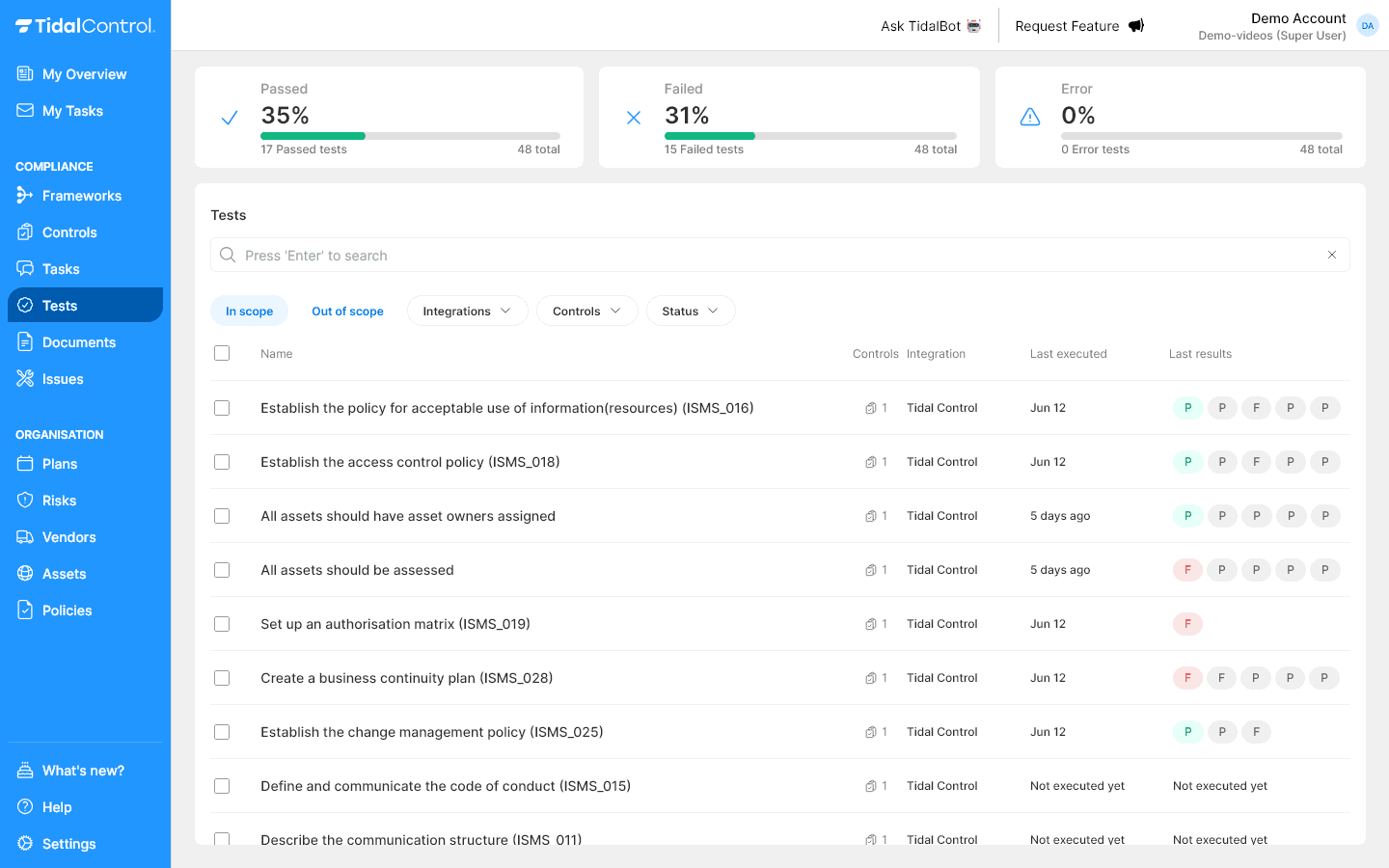
-
Review framework-related tests
-
Analyse Pass/Fail trends
-
Identify improvement points from Failed tests
-
Plan improvement actions for tests that can't be resolved immediately
For test management, see Tests getting started.
Adopt remaining policies
Adapt remaining policy templates:
- Go to Policies section
- Filter on 'Not started' and 'Draft' status to show unfinished policies
- For each policy:
- Open and review template content
- Adapt to organisation context - Make it specific for your situation
- Fill in placeholders - Replace generic text with organisation details
- Submit for approval via "Request Approval"
- Monitor approval workflow - Track status and address feedback
- Communicate approved policies to relevant teams
For more information about policy management, see Policies getting started.
Execute manual tasks
Complete your own control implementation tasks:
- Go to My Tasks section - this is already filtered to your personal tasks
- For each task:
- Review implementation instructions in task description
- Execute required actions according to guidance
- Upload evidence - Documents, screenshots, or certificates
- Document implementation details via task comments
- Update status to 'Completed' when finished
- Validate: no tasks remain open in My Tasks
Monitor team progress:
- Go to Tasks page - To check status of tasks assigned to others
- Monitor blocked tasks approaching deadline - Help team members with obstacles
- Go to My Overview page - For total overview of outstanding work in Tidal
For more information about dashboard and overviews, see Tidal Control documentation.
Check phase
In the Check phase you validate effectiveness of implemented controls and prepare for formal reviews. You check all controls are executed correctly and document findings for management.
Control status monitoring
Get all controls to green:
-
Go to Controls section

-
Review control status overview - Use dashboard for total overview
-
Filter on 'Ineffective' status to identify problematic controls
-
For each control not showing green:
- Open control details - Analyse why status isn't OK
- Check linked tasks - Are all implementation tasks completed?
- Validate evidence - Is documentation complete and current?
- Address issues - Resolve missing elements
-
Validate all controls show 'Status OK' (green)
A control can only get OK status (green) when all linked tasks are completed.
Validate Tidal quality tests
Run through quality checks:
-
Go to Tests section

-
Filter on integration 'Tidal' and status 'Failed' to show failed quality tests
-
For each failed test:
- Review test description - Understand what's being checked
- Analyse why test fails - What's not compliant?
- Correct underlying data - Fix issues in risk analyses, asset assessments, etc.
- Re-run test - Check test now passes
-
Validate all Tidal tests have 'Passed' status
Common problems in Tidal:
- Incomplete risk assessments - Risks without likelihood/impact scores or risk acceptance criteria not filled in
- Missing asset owners - Assets without assigned owner
- Policy gaps - Policies in draft status or not approved
Conduct internal audit
Internal audit preparation:
- Go to Policies section
- Find and open 'Internal Audit Programme' - Review audit process description
- Check all prerequisites are met:
- All controls have OK status
- All Tidal tests are passed
- Policy documentation is complete and approved
Audit execution:
- Plan internal audit - Usually conducted by Tidal consultant
- Follow Internal Audit Programme - According to standardised methodology
- Document findings - Use Tidal reporting template
- Respond to audit findings - Management fills in their initial response to report in reporting template
- Upload reporting and close corresponding assessment task in Tidal to complete process
For more information about internal audits, see Tidal Control documentation.
Conduct management review
Management review execution:
- Plan management review meeting - Invite senior management
- Present findings - Use 'Notes of Management Review' template as agenda
- Create action plans - And document these in meeting minutes
- Upload minutes and close corresponding task in Tidal to complete process
For more information about management reviews, see Tidal Control documentation.
Act phase
In the Act phase you convert findings from Check phase into concrete improvement actions and set up the system for continuous monitoring. You document action points as Issues and configure recurring processes via Plans.
Create issues for findings and actions
Record management action points:
-
Go to Issues section
-
Click 'Add Issue' to create new action points
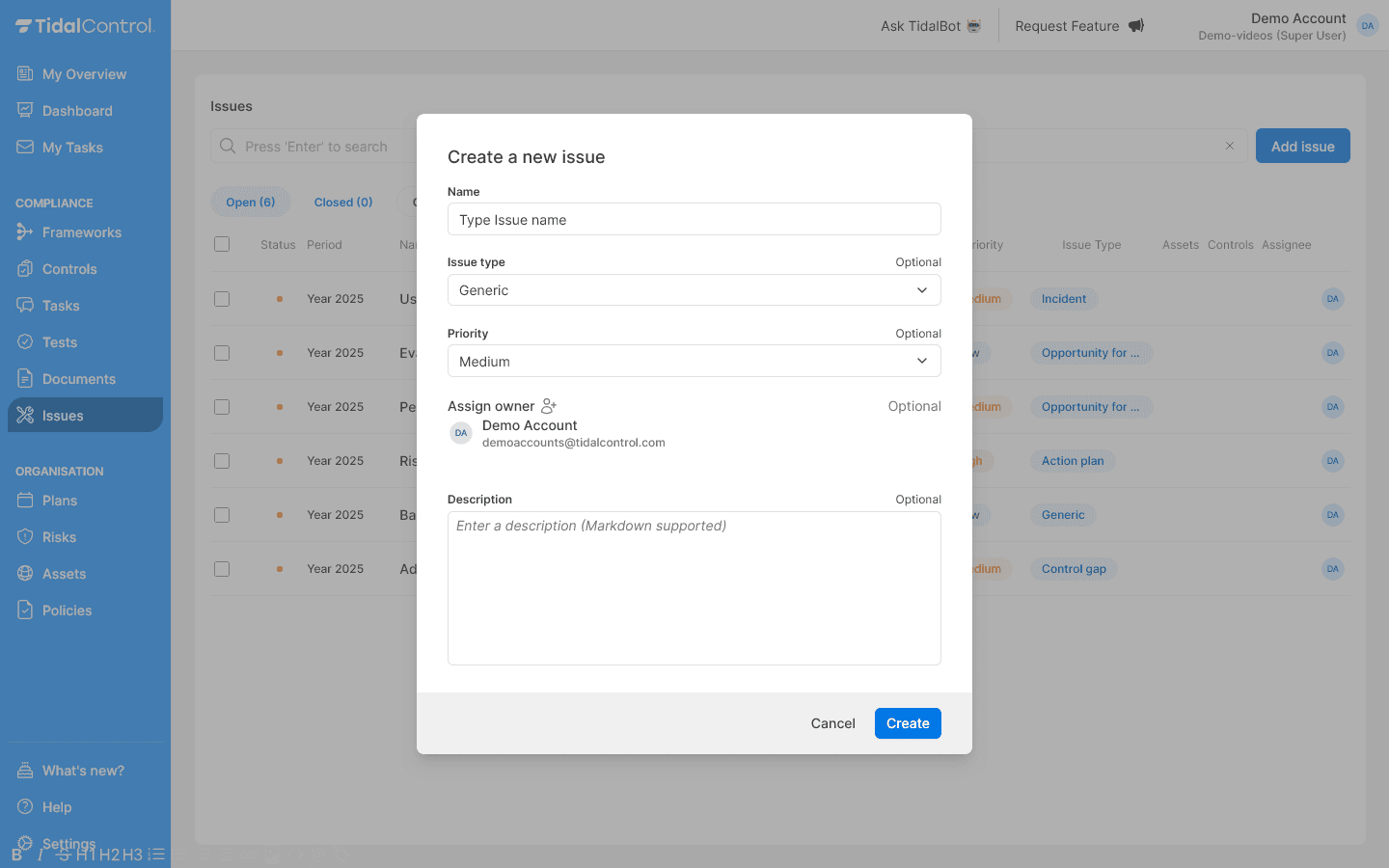
-
For each finding from internal audit and management review:
- Issue title - Short, clear description of action point
- Description - Detailed explanation of finding and desired action
- Assign to - Assign owner (usually management or process owner)
- Due date - Set realistic deadline
- Priority - Determine urgency (High/Medium/Low)
- Link to framework - Link to relevant framework if applicable
-
Monitor progress - Track status of issued action points
-
Update status - Mark issues as 'Resolved' when completed
For more information about issue management, see Issues.
Validate and adjust plans
Review preconfigured Plans: Because you start with a template, essential Plans are already created and configured. You only need to validate settings and adjust where needed.
-
Go to Plans section

-
For each Plan:
- Open Plan details - Click Plan name
- Check 'Creation Date' - Is start date for task generation correct?
- Validate 'Due Date' - Are deadlines realistic for your organisation?
- Check linked Controls - Are correct controls in Plan?
- Redistribute between Plans - Move controls to correct Plan if needed
-
Activate Plans - Ensure all Plans have 'Active' status
-
Review task generation - Check next tasks are created correctly
For detailed Plans configuration, see Plans.
Implement continuous improvement
Prepare next PDCA cycle:
- Review all Issues - Ensure action points are picked up
- Validate Plans - Check automation works correctly
- Document lessons learned - Record experiences for next cycle
- Prepare next cycle - Planning for next PDCA iteration
Success indicators:
- All Issues have owners and realistic deadlines
- Plans are active and generate tasks according to schedule
- Team is trained on new processes and tools
- Framework is operational and delivers continuous compliance value
You now have a fully operational compliance framework with automated monitoring that delivers continuous value to your organisation.
- Previous
- Configuring Single Sign-On (SSO)