Tasks
Creating and managing tasks
Adding new tasks
Creating a task
- Go to the Tasks page via the main menu
- Click "Add task" in the top right of the overview
- The creation form opens where you can fill in task information

Filling in task information
Required fields:
- Name - Choose a clear, descriptive name for the work
- For example: "Perform a management review" or "Test backup procedure"
- Task Type - Select Execution or Assessment
Optional but recommended fields:
- Assign owner - Assign responsible person
- Description - Detailed context and instructions
Clear naming: Use action-oriented names that clearly indicate what needs to be done. "Perform management review" is better than "Review".
Selecting task type
Choosing the right type helps with workflow and assignment:
Execution - For implementation work:
- Execute technical configurations
- Implement procedures
- Provide training
- Install systems
- Example: "Configure new firewall rules"
Assessment - For evaluation work:
- Assess effectiveness
- Conduct audits
- Hold reviews
- Check compliance
- Example: "Assess effectiveness of access controls"
When to choose which type:
- Execution - If you need to build, install, or implement something
- Assessment - If you need to check, assess, or evaluate something
Saving the task
- Check all entered information
- Click "Create" to create the task
- The new task appears in your overview with "Open" status
Editing task details
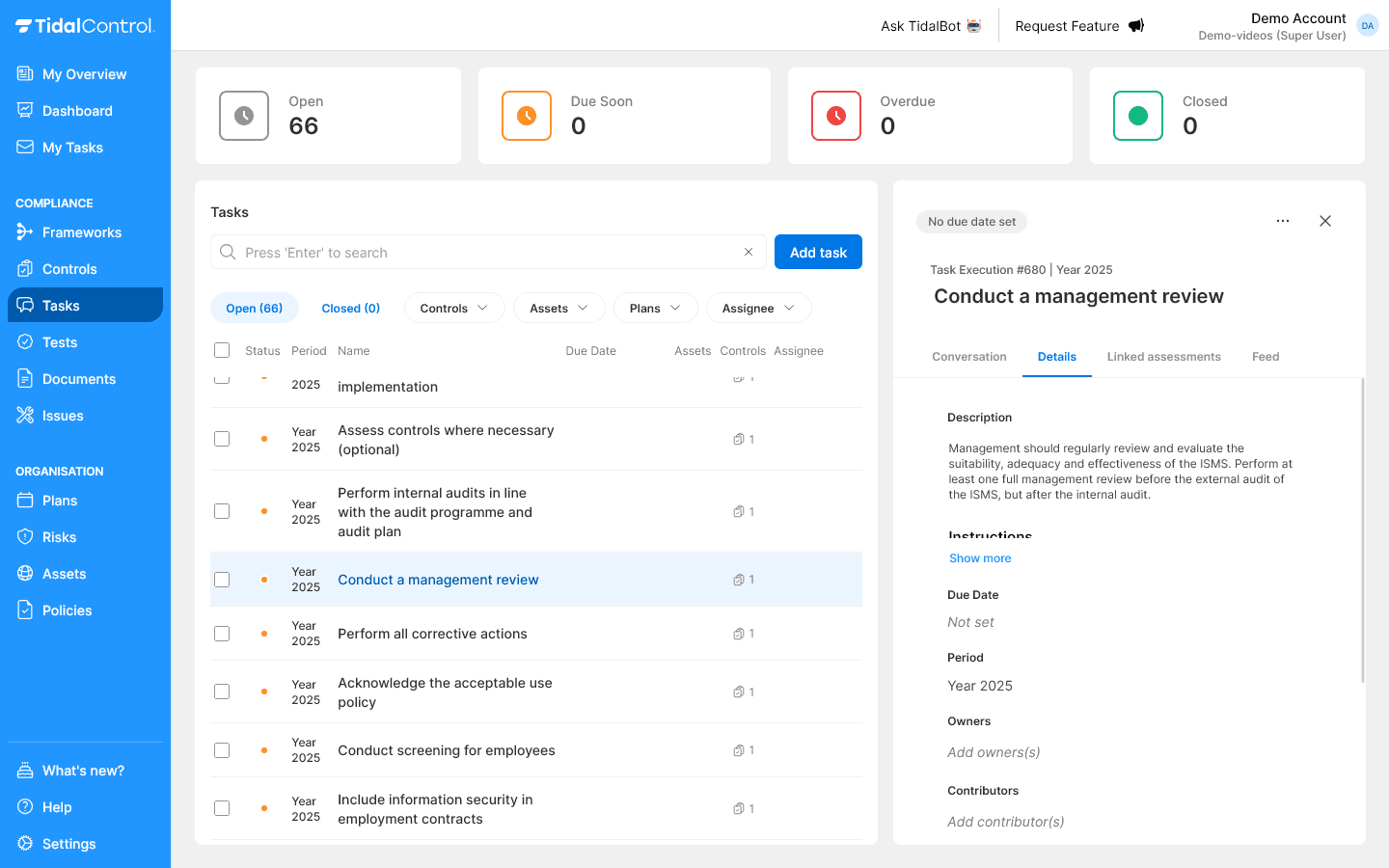
Opening task details
- Click on a task name in the overview
- The details panel opens on the right side
- Select the "Details" tab for editable fields
Editable information
Adjusting basic data:
- Description - Detailed instructions and context
- Due Date - Set deadline for completion
- Period - Time period in which task is relevant
Expanding instructions:
- Step-by-step explanation - What exactly needs to happen?
- Expected result - What is the end result?
- Required resources - What tools or access are needed?
- Acceptance criteria - When is the task completed?
Automatic updates:
- Changes are saved immediately
- Feed tab shows historical changes
- Notifications to involved persons
Owners and responsibilities
Assigning owners
Primary ownership:
- Click in "Owners" section on the right side
- Type username and select from dropdown
- Multiple owners possible for shared responsibility
Owner responsibilities:
- Task planning and resource allocation
- Progress monitoring and quality control
- Final approval of task completion
- Escalation for problems or delays
Adding contributors
Involving executors:
- Click "Add contributor(s)" link
- Select team members working on execution
- Contributors receive automatic notifications
Contributor roles:
- Practical execution of work
- Evidence collection and documentation
- Progress updates via comments
- Collaboration with other stakeholders
Clear roles: Ensure ownership and contributor roles are clear. Owners are ultimately responsible, contributors perform the work.
Deadlines and planning
Setting Due Date
Determining deadline:
- Click "Due Date" field in Details tab
- Select realistic date from calendar
- Consider complexity and available resources
Deadline guidelines per type:
- Execution tasks: Depending on implementation complexity (days to weeks)
- Assessment tasks: Often linked to audit cycles (months)
- Periodic tasks: Automatically set by Plans
- Ad-hoc tasks: Based on urgency and priority
Period management
Setting time period:
- Year 2025 - Default for ongoing tasks
- Periodic tasks: Automatically set by Plans based on Plan frequency
Managing task links
Linking assets
Why link assets:
- Clarify which business assets are involved
- Define impact scope of the work
- Set priorities based on asset criticality
Selecting assets:
- View linked assets in task details
- Assets are often automatically linked via Plans
- Manual adjustments and linking multiple assets possible if needed
Linking controls
Why link controls:
- Clarify which controls the task contributes to
- Task is included in status and progress indicators at control level
- Tracking control status is required for various standards including ISO 27001
Selecting controls:
- View linked controls in task details
- Controls are often automatically linked via Plans
- Manual adjustments and linking multiple controls possible if needed
Linked assessments
What are Linked assessments?
- Only available for Execution tasks
- Shows Assessment tasks with same scope (controls, assets and period)
- Cross-referencing shows relationship between work
Viewing related tasks:
- Click on a task name in the overview
- The details panel opens on the right side
- Select the "Linked assessments" tab for assessment tasks
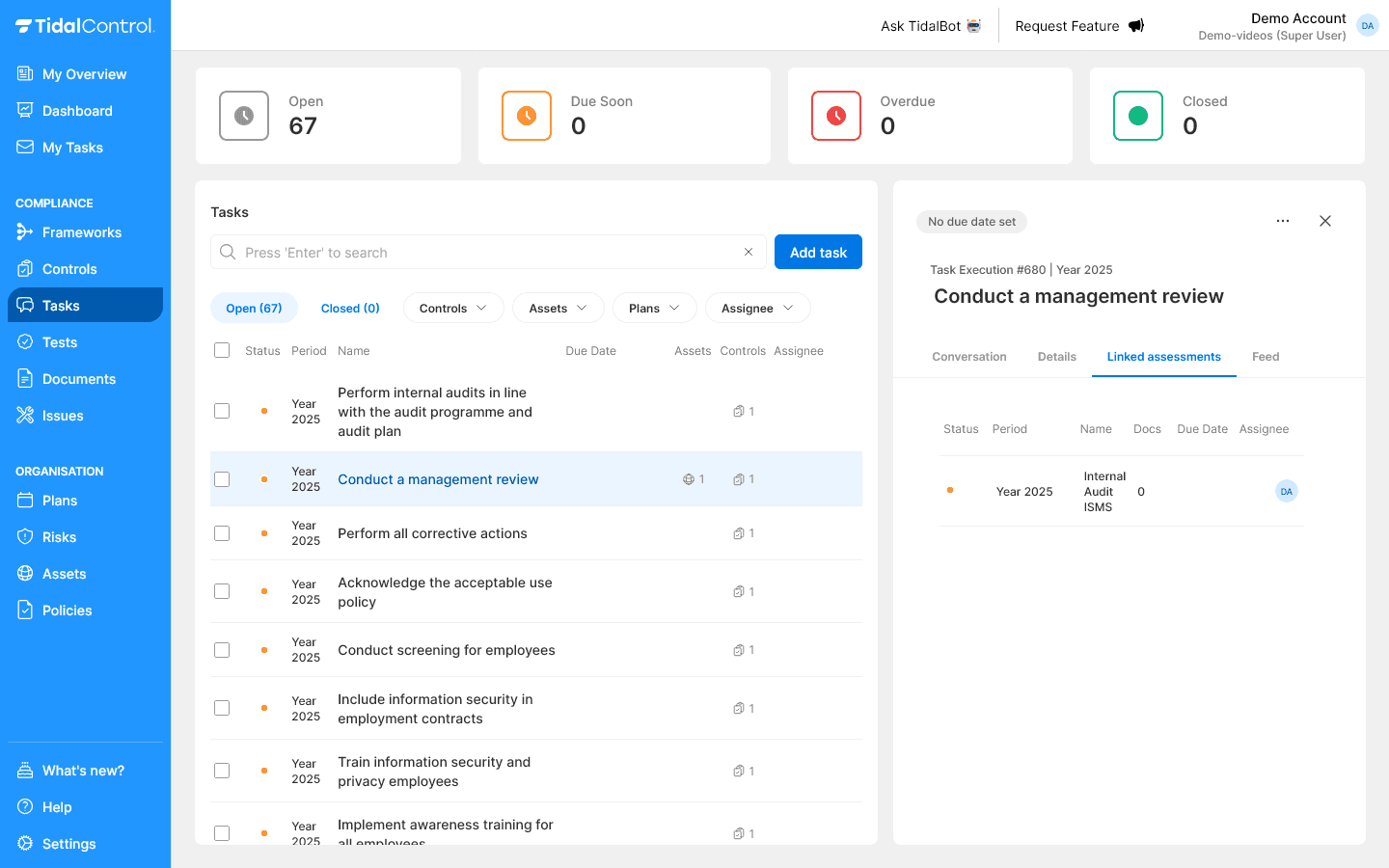
How to use this information:
- Understand workflow - How tasks build on each other
- Map dependencies - Which tasks must be completed first in a workflow
- Total overview - Overview of all related activities
Linked executions
What are Linked executions?
- Only available for Assessment tasks
- Shows Execution tasks with same scope (controls, assets and period)
- Cross-referencing shows relationship between work
Viewing related tasks:
- Click on a task name in the overview
- The details panel opens on the right side
- Select the "Linked executions" tab for execution tasks
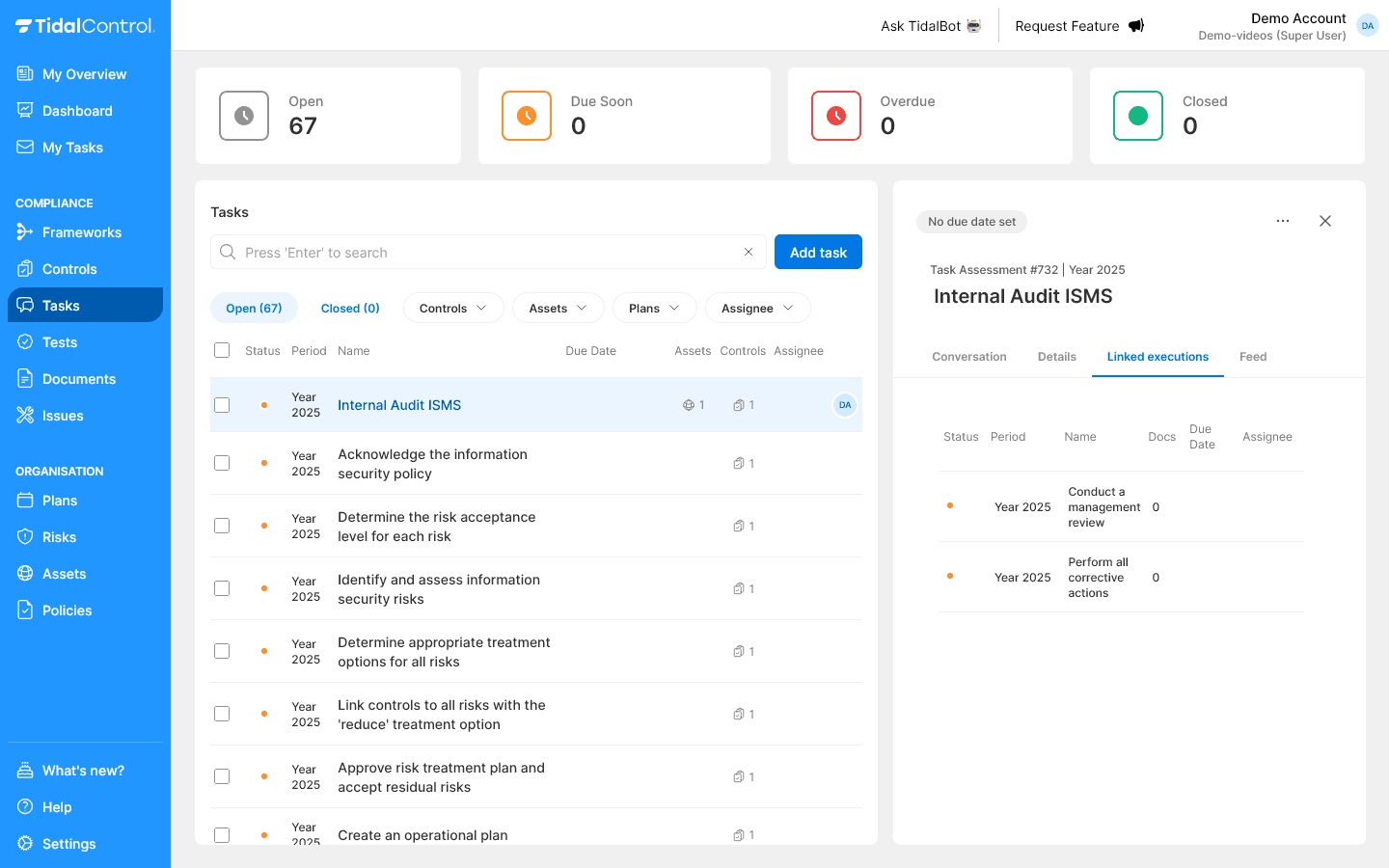
How to use this information:
- Assess all execution tasks - as part of the Assessment task
- Direct link to execution tasks - for review, reopening and other actions resulting from the Assessment
- Total overview - Overview of all related activities and dependencies
Task lifecycle management
Status monitoring
Keep Open status when:
- Work still in progress
- Waiting for evidence or approval
- Dependencies not yet completed
Move to Closed status when:
- All work completed
- Evidence collected and validated
- Owner has approved completion
Automatic task generation
Plans generate tasks:
- Regular cycles - Monthly, quarterly, annually
- Consistent execution - Guaranteed compliance activities
- Template-based - Predefined instructions and criteria
Manual tasks vs Automatic:
- Manual tasks - One-time or ad-hoc work
- Automatic tasks - Periodic compliance activities
- Hybrid approach - Combination for complete coverage
Tasks are often automatically created by Plans linked to Controls (or Assets). This gives you an ongoing cycle of compliance activities without manual planning.
Read more about this in Creating and managing plans
Task templates and standardization
Consistent task creation
Execution template:
Name: [Action] - [Goal/Component]
Description:
- Goal: [What do you want to achieve]
- Steps: [Concrete execution steps]
- Required resources: [Tools, access, time]
- Expected result: [End state]
- Acceptance criteria: [When is it ready]
Assessment template:
Name: [Assessment] - [Subject]
Description:
- Scope: [What is being assessed]
- Method: [How will you assess it]
- Criteria: [What do you assess on]
- Evidence: [What evidence do you collect]
- Reporting: [How do you document findings]
Quality control
Review checklist:
- ☐ Task name is specific and actionable
- ☐ Correct type selected (Execution/Assessment)
- ☐ Owner has capacity and expertise
- ☐ Deadline is realistic and justified
- ☐ Description contains sufficient instructions
- ☐ Expected result is clearly defined
Best practices for task management
Effective planning
Task scoping:
- Atomic tasks - One clear action per task
- Realistic scope - Not too large or complex
- Measurable outcomes - Clear definition of "done"
- Time-boxed - Reasonable deadline with buffer
Team coordination
Promoting collaboration:
- Regular check-ins - Weekly status updates
- Clear communication - Use @mentions for urgent matters
- Share evidence - Upload proof directly upon completion
- Knowledge transfer - Document lessons learned
Workflow optimization
Improving efficiency:
- Group similar tasks - Group similar work
- Automate where possible - Use Plans for repetitive tasks
- Reuse descriptions - Standardize common instructions
- Continuous improvement - Evaluate and optimize processes
Start with standard tasks: Begin with simple, well-defined tasks before implementing complex workflows. Build expertise gradually.
Next steps
Now that you can create and manage tasks:
- Plan your work systematically with realistic deadlines
- Monitor progress via dashboard and notifications
- Collaborate effectively via conversation features
- Document results for audit and compliance
- Previous
- Getting started with tasks