Issues
Creating and managing issues
Adding new issues
Creating an issue
- Go to the Issues page via the main menu
- Click "Add Issue" in the top right of the overview
- The creation form opens where you can fill in non-conformity information
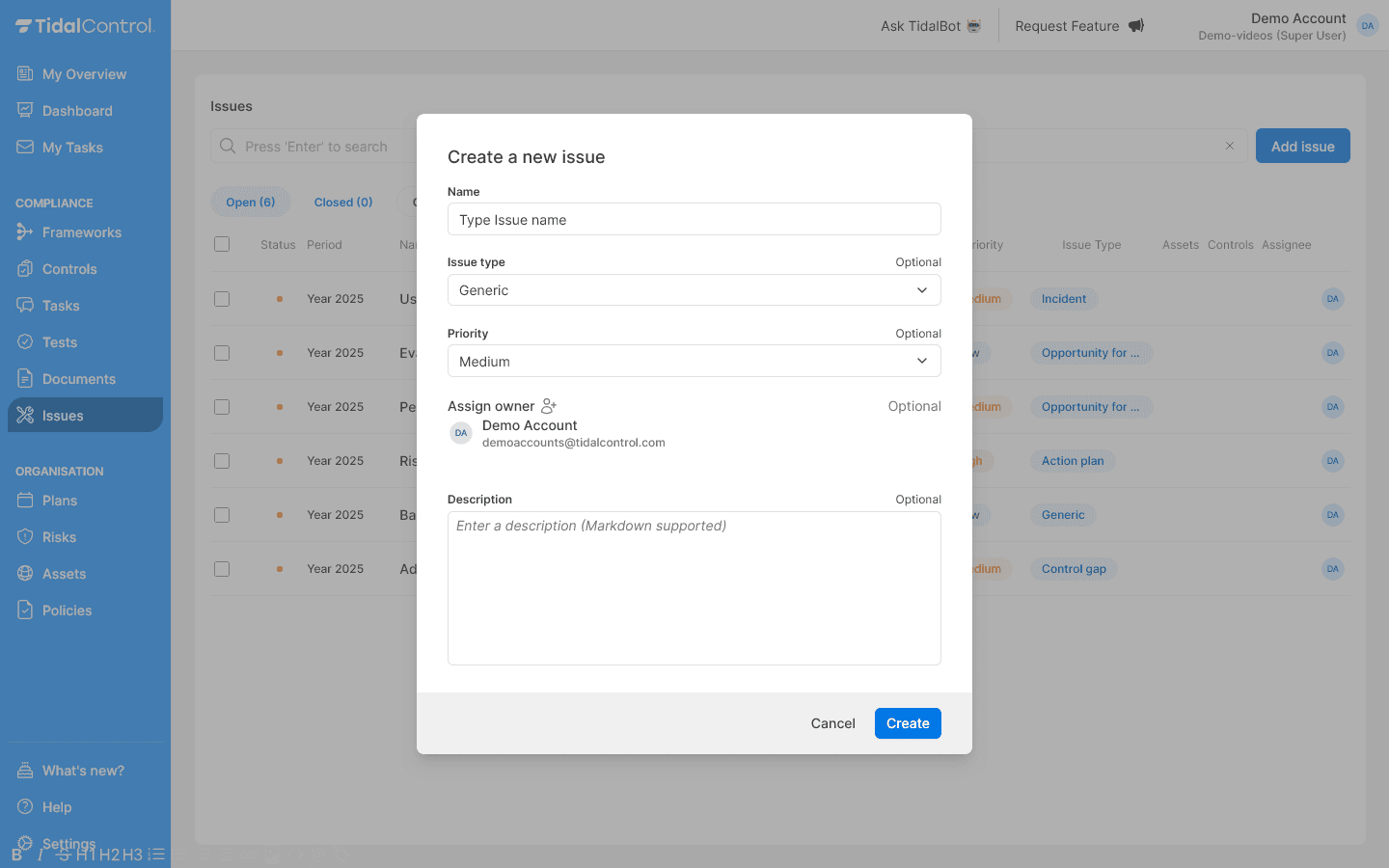
Filling in issue information
Required fields:
- Name - Choose a clear, descriptive name for the non-conformity
- For example: "Employee forgets laptop on train" or "Backup missed on multiple dates"
Optional but recommended fields:
- Issue type - Select the correct category from 7 available types
- Priority - Set urgency (High, Medium, Low)
- Assign owner - Assign responsible person
- Description - Detailed context and background information
Clear naming: Use specific, action-oriented names. "MFA not active for administrators" is better than "Login problem".
Selecting issue type
Choosing the right type helps with workflow, reporting and assignment:
Generic - For general organizational matters:
- Policy needs to be created or updated
- Procedures missing for new processes
- Organizational changes require adjustments
- Example: "Implement employee screening procedure"
Audit finding - For formal audit findings:
- External auditor identifies non-conformities
- Internal audit finds compliance shortcomings
- Certification body sets requirements
- Example: "ISO auditor missing management review documentation"
Control gap - For missing controls:
- GAP analysis shows required controls that are missing
- New risks require additional measures
- Compliance frameworks introduce new requirements
- Example: "Access control admin accounts insufficiently restricted"
Incident - For actual security incidents:
- Phishing attacks and malware infections
- Data breaches and unauthorized access
- Physical security breaches
- Example: "Phishing attack compromises employee account"
Action plan - For planned improvement projects:
- Rollout of new security measures
- Training and awareness programs
- Implementation of new systems
- Example: "Q2 rollout security awareness training program"
Control deficiency - For failing existing controls:
- Implemented controls not working correctly
- Technical problems with security tools
- Process not effectively executed
- Example: "Encryption fails leaving data unencrypted"
Opportunity for improvement - For optimization:
- Efficiency improvements of working processes
- Cost saving opportunities
- User experience improvements
- Example: "Speed up onboarding for faster security training"
Determining priority
Assign High Priority for:
- Compliance deadlines within 30 days
- Critical security risks that directly threaten
- Audit findings that endanger certification
- Active incidents with ongoing impact
Medium Priority for:
- Planned improvements with quarterly deadline
- Control gaps without direct threat
- Action plans with clear planning
- Normal audit findings without urgency
Low Priority for:
- Long-term optimizations (> 6 months)
- Nice-to-have improvements without compliance impact
- Opportunities depending on other projects
- Minor administrative adjustments
Saving the issue
- Check all entered information
- Click "Create" to create the issue
- The new issue appears in your overview with "Open" status
Editing issue details
Opening issue details
- Click on an issue name in the overview
- The details panel opens on the right side
- Select the "Details" tab for editable fields
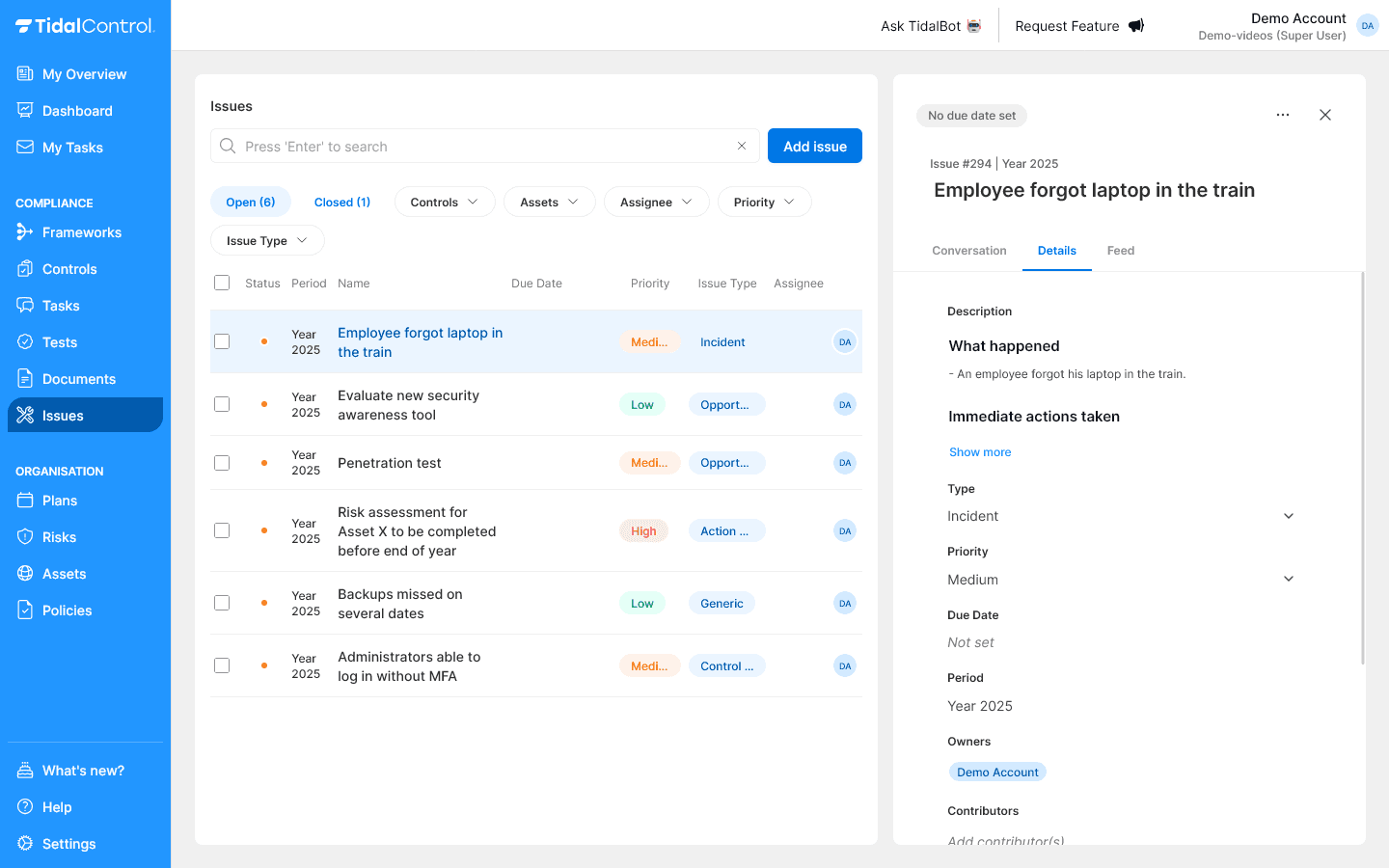
Editable information
Adjusting basic data:
- Description - Detailed background and context
- Type - Change category if incorrectly assigned
- Priority - Adjust urgency based on new insights
- Due Date - Set deadline for solution
- Period - Time period in which issue is relevant
Automatic updates:
- Changes are saved immediately
- Feed tab shows historical changes
- Notifications to involved persons
Owners and responsibilities
Assigning owners
Primary ownership:
- Click in "Owners" section on the right side
- Type username and select from dropdown
- Multiple owners possible for shared responsibility
Owner responsibilities:
- Prioritization of issue resolution
- Resource allocation for execution
- Progress monitoring and escalation
- Final approval of issue closure
Adding contributors
Involving executors:
- Click "Add contributor(s)" link
- Select team members working on solution
- Contributors receive automatic notifications
Contributor roles:
- Technical implementation of solutions
- Evidence collection and documentation
- Testing and validation of fixes
- Progress updates via comments
Clear roles: Ensure ownership and contributor roles are clear. Too many owners can lead to confusion about final responsibility.
Deadlines and planning
Setting Due Date
Determining deadline:
- Click "Due Date" field in Details tab
- Select realistic date from calendar
- Consider complexity and available resources
Deadline guidelines per type:
- Incidents: 1-7 days (depending on severity)
- Audit findings: Before next audit (usually 3-12 months)
- Control gaps: 30-90 days (depending on implementation)
- Action plans: Project timeline (weeks to months)
- Opportunities: Flexible (months to year)
Period management (optional)
Setting time period:
- Year 2025 - Default for ongoing issues
- Custom periods - For multi-year projects
Issue lifecycle management
Status monitoring
Keep Open status when:
- Active work is ongoing
- Waiting for external dependencies
- In review or test phase
- Not yet fully resolved
Move to Closed status when:
- Problem completely resolved
- Measures implemented and tested
- Evidence collected and approved
- Owner has validated closure
Managing issue links
Linking assets:
- Which business assets are involved in this issue?
- Document impact on critical systems
- Determine recovery priorities
Linking controls:
- Which controls are related?
- New controls being implemented
- Existing controls being modified
Bulk operations
Managing multiple issues simultaneously
Available bulk operations:
- Change assignee - Assign new owner to group of issues
- Delete - Remove multiple issues from system at once
Bulk workflow:
- Select issues with checkboxes on left in overview
- Relevant buttons appear at top of table
- Choose desired action and confirm
Not possible for bulk:
- Edit issue descriptions
- Set due dates individually
- Complex relationship management
- Closing
- Adjust Type or Priority
Issue templates and standardization
Consistent issue creation
Template examples per type:
Incident template:
Name: [Incident type] - [Affected system/person]
Description:
- What happened: [Brief description]
- When discovered: [Time]
- Immediate actions: [First response]
- Impact: [Affected systems/users]
- Root cause analysis: [To be investigated]
Audit finding template:
Name: [Auditor finding] - [Affected control/process]
Description:
- Audit details: [Internal/external auditor, date]
- Finding: [Specific non-conformity]
- Required action: [What needs to be resolved]
- Audit reference: [Finding number/section]
Quality control
Review checklist:
- ☐ Issue name is specific and actionable
- ☐ Correct type selected for category
- ☐ Priority fits urgency and impact
- ☐ Owner has capacity and expertise
- ☐ Deadline is realistic and justified
- ☐ Description contains sufficient context
Best practices for issue management
Proactive issue monitoring
Regular sources:
- Monthly system reviews - Monitoring alerts and logs
- Quarterly assessments - Control effectiveness evaluations
- Annual audits - Formal compliance reviews
- Incident analysis - Lessons learned sessions
Effective communication
Issue updates protocol:
- Weekly progress - Brief status update for high priority
- Monthly summary - Overview for medium priority
- Milestone reporting - For significant progress
- Escalation triggers - When deadline is threatened
Continuous improvement
Track metrics:
- Time to resolution - Average resolution time per type
- Recurrence rate - How often similar issues return
- Owner effectiveness - Which assignees resolve fastest
- Root cause patterns - Identify structural problems
Preventive approach: Use issue patterns to develop proactive measures. If many incidents of the same type occur, consider preventive controls.
Next steps
Now that you can create and manage issues:
- Systematically register all non-conformities you encounter
- Monitor deadlines and progress via dashboard
- Collaborate on solutions via comments and evidence
- Analyze trends for preventive improvements
- Previous
- Getting started with Issues